 Capra hircus
Capra hircus
------------
English: Common goat
German: Hausziege
French: Ch‚vre domestique
Spanish: Cabrito
Distribution areas
------------------
Approximately twenty varieties of domes-
tic goat are bred throughout all of the
inhabited continents. The skins come chiefly
from South-East Asia, North Africa and from
South America.
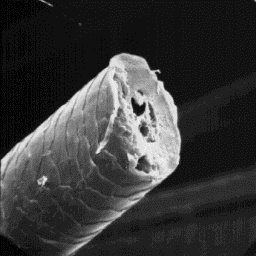
Description of the fur Transverse section
---------------------- of an intermediate fibre, 600x
The coat of the continental goat is
usually white and mostly consists of coarse straight fibres although a small
number of fine fur fibres are also present. The goat skins from Arabian
countries have finer hairs fibres, often crimpled and black, black and white
(spotted), or grey in colour. The Chinese and East-Indian goat skins have
hair of a lustrous appearance and the coat is usually grey, brown or of some
intermediate shades. The finest furs are from Cashmere and Angora goat skins.
|
|
 Capra hircus
Capra hircus
------------
English: Common goat
German: Hausziege
French: Ch‚vre domestique
Spanish: Cabrito
The coat of the continental goat is
usually white and mostly consists of coarse
straight fibres although a small number of
fine fur fibres are also present. The goat
skins from Arabian countries have finer
hairs fibres, often crimpled and black,
black and white (spotted), or grey in
colour. The Chinese and East-Indian goat
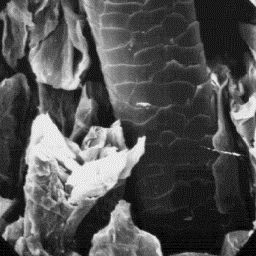
skins have hair of a lustrous appearance and The cuticular structure
the coat is usually grey, brown or of some of an intermediate hair, 600x
Goat skins are very variable in size; the
smallest ones are about 60 cm long and the biggest more than 180 cm long. The
hairs of common goats are generally coarse but the coats also contain a
proportion of finer fur fibres which are soft to the touch. An undercoat
cannot be distinguished as separate layer. The length of the longest hairs
varies from 35 to 80 mm, or more in some cases.
|
|
 Capra hircus
Capra hircus
------------
English: Common goat
German: Hausziege
French: Ch‚vre domestique
Spanish: Cabrito
Structure of the hair
---------------------
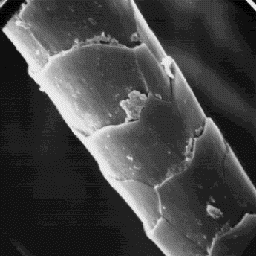
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface appears furrowed. The openings of
the hair follicles are narrow with raised
edges. The hairs usually emerge from the
follicles in groups of 5 to 8; only the
coarse guard hairs are single.
The cuticular structure
The fine fur fibres are from 10 to 20 µm of the fine fibres, 2000x
in diameter and their cross-sections are
circular in shape. The cuticular scale pattern is of the cornet-like type,
with both the surface and the margins of the scales being smooth. Only in a
few cases is the scale surface slightly grooved. Some fine fur hairs are
non-medullated but the fibres mostly have a central symmetrical type of
medulla, which is narrow, unbroken and of the lattice-sponge-like type. The
medullar infilling substance is of the foam-like, fibrous or amorphous
structure.
|
|
 Capra hircus
Capra hircus
------------
English: Common goat
German: Hausziege
French: Ch‚vre domestique
Spanish: Cabrito
The intermediate fibres have similar
microscopical features to the guard hairs,
except that their-cross-sectional diameters
are smaller, only about 30 to 60 µm, and
the cuticular scale margins are usually
straight.
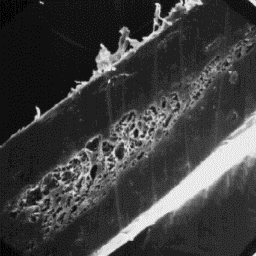
The guard hairs are nearly circular is
cross-sectional outline, and from 70 to 120 Longitudinal section
µm in diameter. The cuticular-scale pattern of a guard hair, 400x
is mosaic with a smooth scale surface and
crenated scale margins. The medulla of the coarse hairs is of the central
symmetrical shape and is usually narrow and unbroken. In only few cases do
the guard hairs contain a medulla of the wide type. The medullar pattern is
of the lattice-sponge-like type with an inner medullar substance of a
foam-like structure.
|
|
 Capra hircus
Capra hircus
------------
English: Common goat
German: Hausziege
French: Ch‚vre domestique
Spanish: Cabrito
Longitudinal section
of an intermediate fibre, 400x
Numerical code for goat skin structure
--------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-5-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5-1.3-1-3.4-1-1-11-5.7-10.21-10.25
Intermediate fibres: 1-2-1-1-3-1-1-11-5-30.61-20.41
Guard hairs: 1-2-1-2-3-1-1-11-5-70.121-20.61
|




